What Do Plant Cells Have During Cell Division That Animal Cells Do Not?
Abstract
If yous alive in an apartment or a house, you will discover that your dwelling has unlike rooms separated by walls. A establish is just like your home, except at that place are many modest rooms, called cells. Plant cells, similar rooms, are also separated past prison cell walls. Prison cell walls are unique and are not establish in creature cells. In a building, if you desire to turn 1 large room into two pocket-size rooms, y'all build a new wall to divide it. This is similar to how a establish cell divides into two cells during cell division. To build a wall in a edifice, you demand to apply construction workers, blueprint the building plan, buy building materials, and finally assembly the wall. How does the establish cell take intendance of these unlike jobs? This commodity explains how the cell wall is congenital in a plant cell during prison cell division.
What is a Plant Cell Wall?
For both plants and animals to grow, their cells must split to produce more than cells. In the process of cell division, i cell becomes two. This process is different in plant and animal cells because establish cells take cell walls . When you look at a plant root through a microscope, you will find that the root looks like a filigree (Figure 1A). Each square in the grid is 1 jail cell. When taking a closer expect at the jail cell purlieus, you tin see that a structure separates one cell from its neighbor cells. This is the jail cell wall. In addition to separation, found jail cell walls as well provide physical support to the cells and protection from pathogens that want to invade the cells. For establish cells to divide, a new cell wall must be built to create two cells from i. The process of edifice a new prison cell wall to split up the dividing plant prison cell is chosen plant cytokinesis .
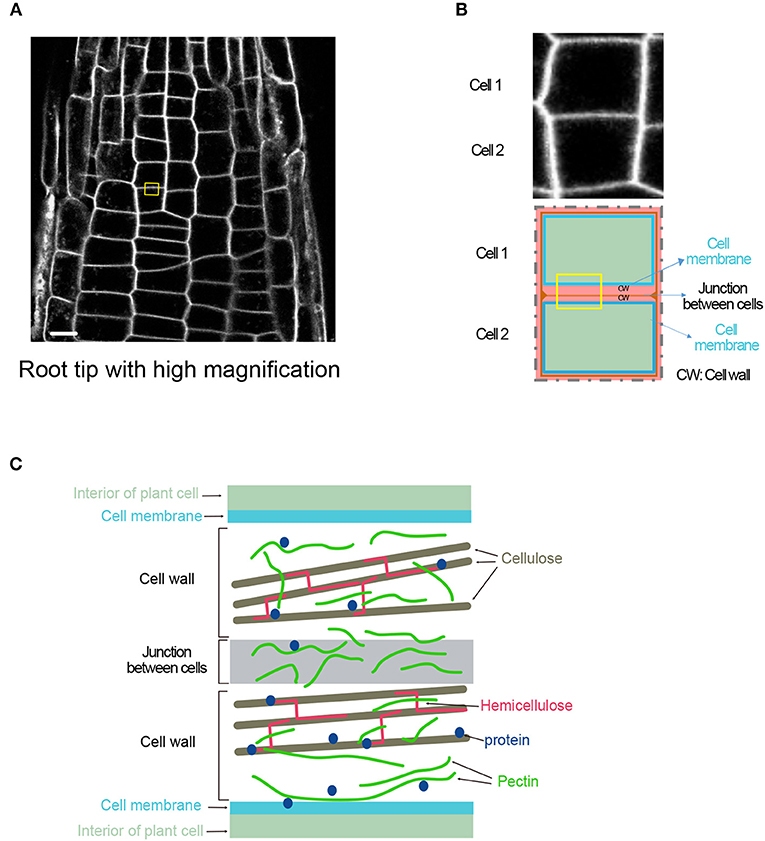
- Figure 1 - Jail cell walls split up institute cells.
- (A) Root tip cells look like a grid under the microscope, due to the clearly visible cell walls. The scale bar measures 0.01 mm. (B) Zooming in on the yellow box in (A), you can meet that the cell walls completely surround each cell. (C) Zooming in even further on the yellowish box in (A) shows that the cell wall contains edifice blocks made of sugar polymers, such as cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin, and proteins.
How Does the Cell Choose the Building Site?
In a building, you can draw marks on the ground and walls to show the workers where to build the new wall. In a plant prison cell, a structure called the preprophase band marks the division zone when the jail cell is near to divide (Figure 2A). Structures called microtubules and microfilaments make up the preprophase band. In one case the division zone is formed, the preprophase band disappears. Just the jail cell still "remembers" the location of the division zone, so that information technology can guide the workers in the cell to the site where the new cell wall should be built.
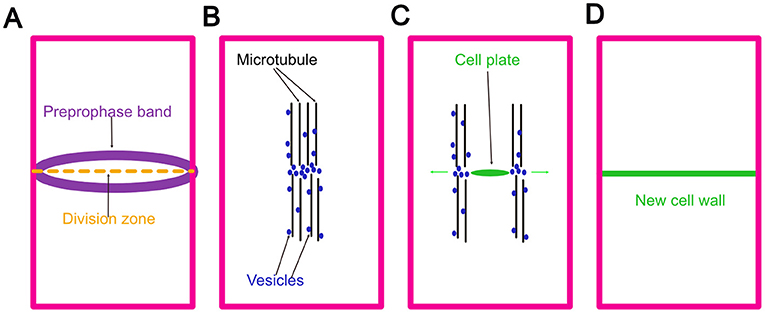
- Figure 2 - Plant cytokinesis is completed by building a new jail cell wall.
- (A) The preprophase ring marks the partition zone, and so that the cell knows where to build the new wall. (B) Vesicles carry cell wall building materials and the protein "workers" along tracks called microtubules to the division zone. (C) Vesicles fuse together in the center of the segmentation zone and form the prison cell plate, which is the beginning of the cell wall. Equally materials are added, the cell plate expands toward the existing wall. (D) When the new cell wall is completed, i big cell becomes two minor cells.
What Are the Building Materials for the Prison cell Wall?
Edifice blocks are the major components of walls in some buildings, and concrete is the textile that sticks those blocks together. In plant cell walls, in that location are various edifice blocks, such every bit cellulose, hemicellulose, and callose. For the concrete, the cells are idea to utilise a substance called pectin . All three building blocks and the physical are made of dissimilar types of sugars. Cellulose is the major reinforcement for the cell wall. Cellulose in the cell wall is organized into potent beams called microfibrils. Cellulose microfibrils function as the backbone of the cell wall (Figure 1C). Pectin, the concrete of the establish cell wall, is more flexible than cellulose, and it allows the jail cell wall to extend. Hemicellulose branches connect the cellulose beams and are all surrounded by bendable pectin strings, to form a potent network. A special edifice block called callose is merely used temporally in the new cell wall, to stabilize the structure site and to make sure the other building blocks are laid down properly [one, 2]. In improver to these saccharide-made blocks and concrete, the cell wall besides has many proteins scattering throughout. Some of these proteins are involved in helping the cell wall change and grow. Just many of the functions of these proteins are still unknown.
Preparation for the Blocks, Physical, and Workers
In a edifice, the materials for constructing walls are fabricated by construction supply companies and and then delivered to the edifice site. Plant cells cannot obtain edifice materials from outside; instead, the cells make the blocks and concrete themselves. Pectin and hemicellulose are made in a membrane structure called the Golgi apparatus that works as a factory of sugar polymer production. Pectin and hemicellulose are delivered to the building site in vesicles , which are packages made of membranes. Cellulose and callose are fabricated at the building sites.
The workers who build the cell wall are proteins that are besides fabricated in the cell. These proteins are assigned specific jobs, including the making of edifice materials, delivery of materials, and associates of the cell wall. Each protein is just responsible for one specific job. For example, the protein chosen KNOLLE is responsible for the fusion of the vesicles together at the building site [three] (Figure 3A).
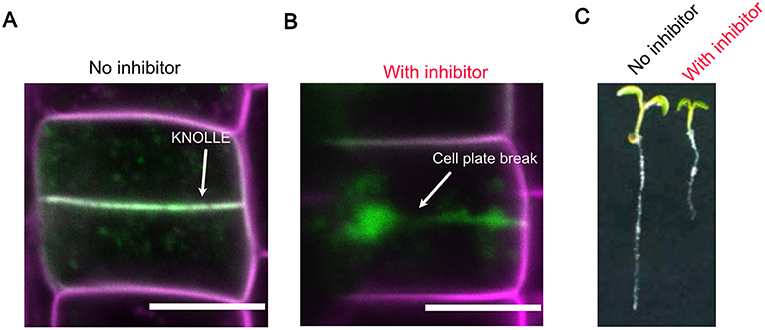
- Effigy iii - Cytokinesis is essential for constitute growth.
- (A) Successful cytokinesis with no chemical inhibitor. The worker protein KNOLLE, shown in fluorescent greenish, is found in the cell plate and the newly forming cell wall. (B) With the addition of a chemical inhibitor, cytokinesis fails and the new cell wall is not completed. In (A,B), the scale bar measures 0.01 mm. (C) Overall, the chemical inhibitors of cytokinesis clearly inhibit constitute growth.
How Does the Cell Assemble the Cell Wall?
The jail cell divides the workers and the materials into ii zones, i on each side of the edifice site. Each zone starts by building delivery tracks fabricated of microtubules. Adjacent, blocks, concrete, and workers are delivered forth the microtubule tracks via vesicles to the building site (Figure 2B). Workers connect vesicles together to outset building the new cell wall. When enough vesicles are continued, it makes a structure called the jail cell plate (Figure 2C). You can retrieve of the prison cell plate equally an intermediate cell wall, more than flexible than the final wall, that remains until structure is finished.
In a building, walls of blocks and concrete are built from the bottom to the height. Plant jail cell walls, interestingly, are built from the heart moving outwards. The new jail cell wall expands from the center point to the edge of the old prison cell wall. At the beginning of jail cell wall construction, the vesicles are delivered to the center betoken, handing off materials to the workers. As the cell plate expands, the delivery tracks and vesicle commitment sites expand (Effigy 2C). In this way, the vesicles are ever delivered to the edge of the cell plate. Expansion does non stop until the cell plate meets the old cell wall. Finally, the new wall is completed, and one big cell becomes two smaller cells (Figure 2D). As the prison cell wall continues to mature, the central layer of the prison cell plate, which has a lot of pectin, helps gum neighboring cells together [2, 4, v] (Figures 1B,C).
Why is Information technology Important to Study Constitute Cytokinesis?
Why is establish cytokinesis so important to study? Tin plants abound without it? To answer these questions, we use chemical inhibitors to disrupt it. With a chemical inhibitor, the structure of the new cell wall is disrupted, leaving a gap in the eye (Figure 3B). If y'all look at the entire establish after treatment with the chemical inhibitor, the root is much shorter than the plant root without the inhibitor (Figure 3C). This experiment tells us that defects in new cell wall structure deadening downward establish growth. Institute cannot grow without establish cytokinesis. Without it, the new prison cell wall volition not be completed, the two minor cells volition non be separated and the plants volition not survive.
Based on further investigations, nosotros know that this chemical inhibitor simply disrupts the usage of callose [6], one of the cell wall building blocks. Every bit you know, plant cytokinesis needs more blocks than only callose. Any fault in the production, commitment, or assembly of any of the cell wall materials or workers will cause problems in plant cytokinesis. I of the applications for this noesis is to develop herbicides. Several herbicides that are used to impale weeds are based on inhibiting cytokinesis.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the NSF Grant MCB 1818219 and U.S. Section of Agriculture award CA-D-PLS-2132-H to GD. Nosotros thank Dr. Destiny J. Davis for reading and editing this manuscript.
Glossary
Prison cell Wall: ↑ A wall surrounding plant cell that can provide structural support and protection to the prison cell.
Plant Cytokinesis: ↑ A process of edifice a new cell wall to separate the dividing plant cell.
Preprophase Band: ↑ A structure made of microtubules and microfilaments that can mark the prison cell partitioning zone when the cells are about to divide.
Microtubules: ↑ Ane kind of protein polymers constitute in plant and animal cells that can provide structural back up to the cell and too function as a delivery track for transportation inside the cell.
Pectin: ↑ A type of saccharide polymer that can exist constitute in cell walls and has gluey properties.
Cellulose: ↑ A type of sugar concatenation that functions as the major reinforcement for the cell wall.
Vesicles: ↑ A blazon of packet that is fabricated with membrane and can carry cargos from 1 place to another within a cell.
Prison cell Plate: ↑ An intermediate structure formed during plant prison cell division that matures into a new cell wall.
Disharmonize of Interest
The authors declare that the inquiry was conducted in the absence of any commercial or fiscal relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
[one] ↑ Drakakaki, Grand. 2015. Polysaccharide degradation during cytokinesis: challenges and hereafter perspectives. Plant Sci. 236:177–84. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.03.018
[two] ↑ Samuels, A. L., Giddings, T. H., and Staehelin, L. A. 1995. Cytokinesis in tobacco BY-two and root tip cells: a new model of cell plate formation in higher plants. J. Cell Biol. 130:1345–57. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.6.1345
[iii] ↑ Lauber, M. H., Waizenegger, I., Steinmann, T., Schwarz, H., Mayer, U., Hwang, I., et al. 1997. The Arabidopsis KNOLLE protein is a cytokinesis-specific syntaxin. J. Cell Biol. 139:1485–93. doi: 10.1083/jcb.139.6.1485
[4] ↑ Smertenko, A., Assaad, F., Baluška, F., Bezanilla, Grand., Buschmann, H., Drakakaki, G., et al. 2017. Plant cytokinesis: terminology for structures and processes. Trends Cell Biol. 27:885–94. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2017.08.008
[v] ↑ Corral-Martínez, P., García-Fortea, E., Bernard, S., Driouich, A., and Seguí-Simarro, J. Thou. 2016. Ultrastructural immunolocalization of arabinogalactan protein, pectin and hemicellulose epitopes through another evolution in Brassica napus. Institute Jail cell Physiol. 57:2161–74. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcw133
[6] ↑ Park, Due east., Díaz-Moreno, Southward. M., Davis, D. J., Wilkop, T. E., Bulone, 5., and Drakakaki, G. 2014. Endosidin 7 specifically arrests late cytokinesis and inhibits callose biosynthesis, revealing distinct trafficking events during cell plate maturation. Plant Physiol. 165:1019–34. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.241497
Source: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/570769
Posted by: haasaftess.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Do Plant Cells Have During Cell Division That Animal Cells Do Not?"
Post a Comment